



Next: Bibliography
Up: Introduction to Low Pressure
Previous: Damage Measurements
Contents
Index
- Crust.
- During high dose implantation using photo-resist masks, the
implanted species (especially heavy ones like arsine) transfere
the upper layer of the resist to pure carbon by knocking out
hydrogen, this is lyer is called crust. During subsequent heat
treatments (e. g. the stripping process) remaining solvent in the
resist below the crust might expand and cause explosions that
form particles. This phenomena is usually called popping.
- Etching Rate.
- The amount of material removed per unit time in an arbitrary
direction from the surface, given e. g. in nm/s or
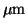 /min.
Depending on
the etching process the etching rate in horizontal and vertical
/min.
Depending on
the etching process the etching rate in horizontal and vertical
- Interconnect.
- Lithography.
- Mask.
- Mask
- Pattern Transfer.
- During the fabrication of an typical IC several different layers
with different structures must be created to form the entire IC
![[*]](crossref.png) .
.
- Photo-resist (PR).
- A organic material which is typically coated onto the surface
by a spin on process. The photo-resist changes its chemical
properties by exposure to light of a suitable wavelength.
Depending on the material the exposed or non-exposed parts
can be wet etched or developed by an appropriate solution.
- Polymer.
- A rather poorly defined term, very widely used in plasma
etching to denote something not perfectly known,
deposited from the plasma to protect sidewalls, achieve high
selectivity or to the other side, form films on the chamber
creating particles. In general a polymer is a chain
formed from smaller molecules, in plasma etching polymers
consist mainly from some coumpounds out of the following list:
carbon (from the resist mask), flourine, hydrogen, metals
(redeposited from the etch process). But also Si-O-Cl or
Si-Br-O compounds deposited for sidewall passivation in
poly etching are called polymers. Polymers are usually
difficult to remove and are a real challange for the stripping
process.
- Selectivity.
- The ratio of the etch rates of different materials under the same
process conditions. In practice this
is an important issue, consider e. g. an insulating layer of silicon
oxide over silicon which should be etched through without
damaging or removing the substrate.
- Sputtering.
- Removal of material ..




Next: Bibliography
Up: Introduction to Low Pressure
Previous: Damage Measurements
Contents
Index
back to www.gs68.de
Other important things: Legal Notice, Contact us
Copyright © 2001-2012 Spitzlsperger Technologies GmbH
![[*]](crossref.png) .
.
![[*]](crossref.png) .
.